
Basic Conditions for Metal Cutting
Relative Motion
The relative motion between the tool and the workpiece is a necessary condition for cutting.
The cutting motion can be divided into primary motion and feed motion.
Primary motion refers to the main relative motion between the tool and the workpiece, ensuring that the tool removes metal at a certain cutting speed.
Feed motion complements the primary motion and enables the sequential and continuous removal of excess metal material.
Read more
Cutting Angles
Different angles are designed to meet various cutting requirements.
There are many cutting angles, and each angle has a different influence on the cutting process.
Common cutting angles include rake angle, clearance angle, principal cutting edge angle, and inclination angle.
Material Properties
The performance of the tool material must meet the cutting requirements for specific workpiece materials.
Common tool materials include high-speed steel, cemented carbide, ceramics, cubic boron nitride, polycrystalline diamond, and more.
Common classifications of workpiece materials include steel, stainless steel, cast iron, superalloys, non-ferrous metals, non-metals, and others.
Read more
System Rigidity
The cutting system consists of machine tools, tools, fixtures, workpieces, and more.
The overall rigidity of the system is crucial for achieving stable cutting.
Components of the Cutting System
Workpiece
Workpiece material, heat treatment condition, shape, machining allowance, machining requirements, and more.
Tool
Tool type, tool material, chip breaker design, tool angles, tool overhang, tool holder connection, cutting parameters, and more.
Machine Tool
Machine tool type, machine tool structure, machining method, spindle type, power torque, cooling supply, and more.
Fixture
Fixture structure, system rigidity, chip evacuation space, and more.
Basic Elements of Cutting
Cutting Force
During machining, the tool needs to overcome the resistance caused by the formation of the chip in the workpiece material.
Cutting Heat
During machining, cutting heat mainly originates from the work done by the tool in causing elastic and plastic deformation in the material of the cutting zone.
Chip Formation
Different types of chip formation not only affect the handling and transportation of chips but also impact the machining quality and tool life.
Basic Parameters of Cutting Motion
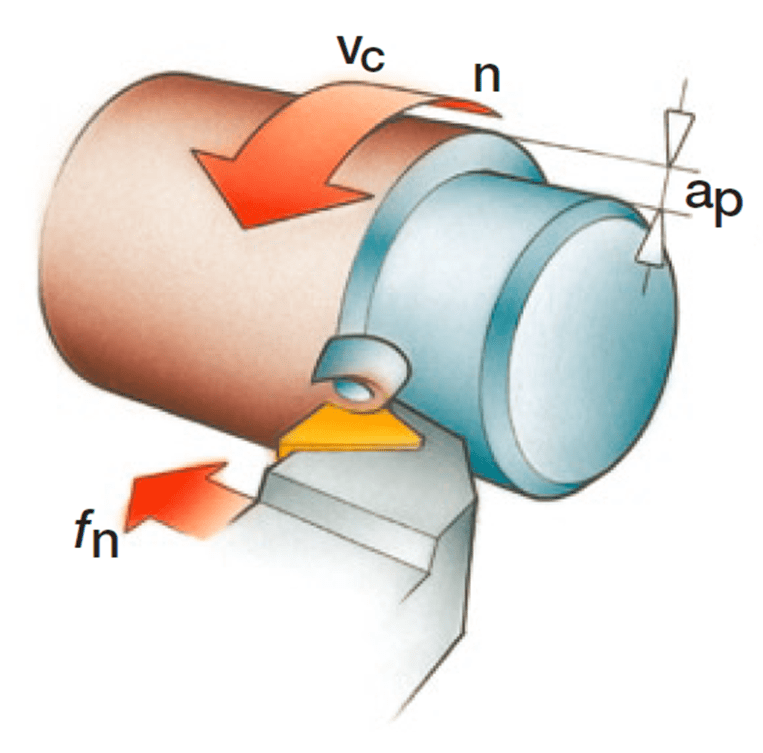
Cutting Speed (vc) (m/min)
The main motion speed of a specific point on the cutting edge relative to the workpiece during cutting.
Feed Rate (vf) (mm/min)
The feed motion speed of a specific point on the cutting edge relative to the workpiece during cutting.
Cutting Depth (ap) (mm)
The perpendicular distance between the machined surface and the surface to be machined on the workpiece.
