Workpiece materials are primarily composed of metals, and in recent years, with the advancement of material technology, many new materials have emerged. When selecting cutting tools for machining, it is essential to understand and differentiate the cutting characteristics of different workpiece materials.
According to cutting characteristics, ISO standards classify workpiece materials into several categories.
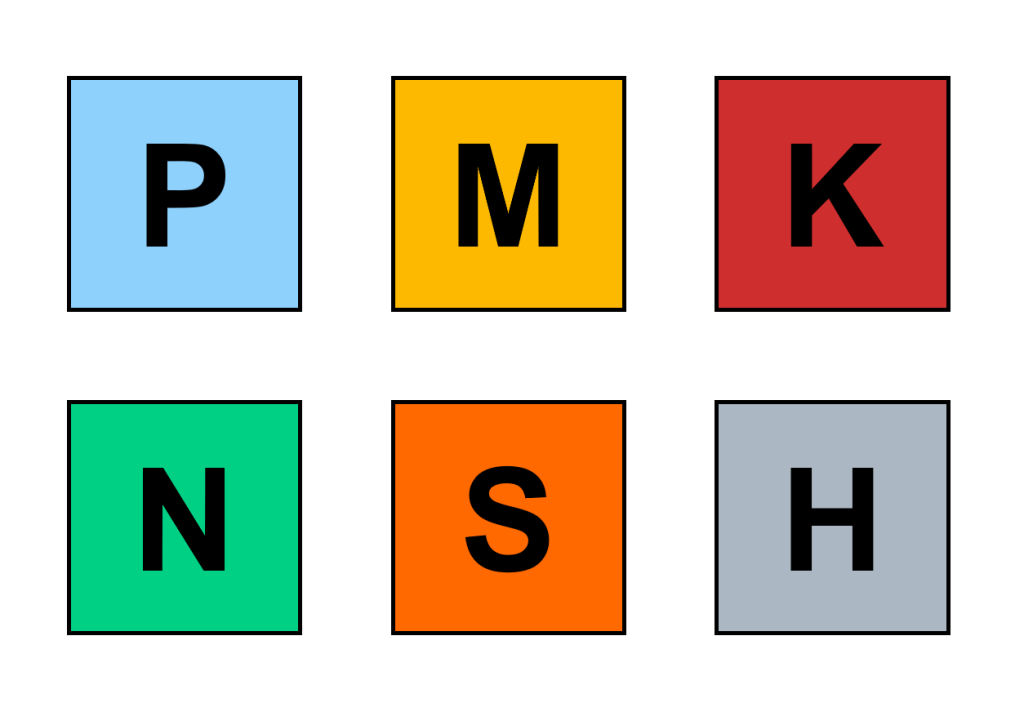
P – Steel
P01-P50
All kinds of steel and cast steel except stainless steel with an austenitic structure.
Cutting Characteristics
During cutting, it is prone to the formation of longer chips. The main factor determining the chip formation is the carbon content of the material. Lower carbon content tends to result in the formation of longer chips.
M – Stainless Steel
M01-M40
Stainless austenitic and austenitic/ferritic steel and cast steel.
Cutting Characteristics
Compared to P-class alloy steels, stainless steels require greater cutting forces, resulting in longer chips that are prone to sticking to the tool. Chip breaking is more challenging. During cutting, the formation of built-up edge and work hardening of the machined surface are common phenomena.
K – Cast Iron
K01-K40
Grey cast iron, cast iron with spheroidal graphite, malleable cast iron.
Cutting Characteristics
Generally, cast iron tends to produce fragmented chips, especially in the case of gray cast iron, which may even result in powdery chips. The chips from ductile cast iron resemble those from alloy steels.
N – Nonferrous Metals
N01-N30
Aluminum and other non-ferrous metals, non-metallic materials.
Cutting Characteristics
This category of materials requires less cutting force. The formation of chips varies significantly depending on the material. Materials with lower alloy proportions, such as pure aluminum and pure copper, tend to stick to the tool more easily.
S – Super Alloys
S01-S30
Heat-resistant special alloys based on iron, nickel and cobalt, titanium and titanium alloys.
Cutting Characteristics
Cutting such materials requires higher cutting forces and power. The chips are longer, prone to sticking to the tool, difficult to break, and challenging to control.
H – Hardened Metals
H01-H30
Hardened steel, hardened cast iron materials, chilled cast iron.
Cutting Characteristics
Generally, the chip temperature is high, resulting in spark-like chips. The tool requires high hardness to withstand the cutting demands.
O – Non-Metallic Materials
Plastics, fiberglass, carbon fiber, graphite, and other non-metallic materials
Cutting Characteristics
The cutting characteristics and chip formation of different non-metallic materials vary significantly, without a typical pattern.
The numbers following the material classification letters, such as P01-P50, represent the different requirements that the cutting conditions impose on the tools for cutting these materials. Generally, a higher number indicates a higher demand for tool toughness and impact resistance, while a lower number indicates a higher demand for tool hardness and wear resistance. This allows for further classification of the same type of material.
Different tool manufacturers, based on their own understanding and rules, classify specific material grades to facilitate users in selecting tools and cutting parameters based on the workpiece material. There can be significant variations in classification among different manufacturers.
For example, the same 316 stainless steel is classified as M05.21 by Sandvik Coromant, M2 by SECO, and M1 by Walter. When selecting tools and cutting parameters across different brands, it is essential to pay attention to these differences.
Additionally, for the same workpiece material, there can be significant variations in cutting performance due to different manufacturing processes and heat treatment states. For example, different processing methods such as casting, forging, rolling, and cold drawing can result in significant differences in the cutting characteristics of 316 stainless steel. Similarly, annealed and unannealed 316 stainless steel will also exhibit different cutting characteristics.
