During cutting operations, the relative motion between the tool and the workpiece can be classified into two categories:
Primary Motion
The primary relative motion between the tool and the workpiece ensures the basic cutting action of removing excess material at a certain speed.
Key parameter: Cutting speed (vc) (m/min)
Feed Motion
The feed motion complements the primary motion and enables the sequential and continuous removal of excess material.
Key parameter: Feed rate (vf) (mm/min)
Different cutting processes may have variations in the forms of cutting motion.
Turning
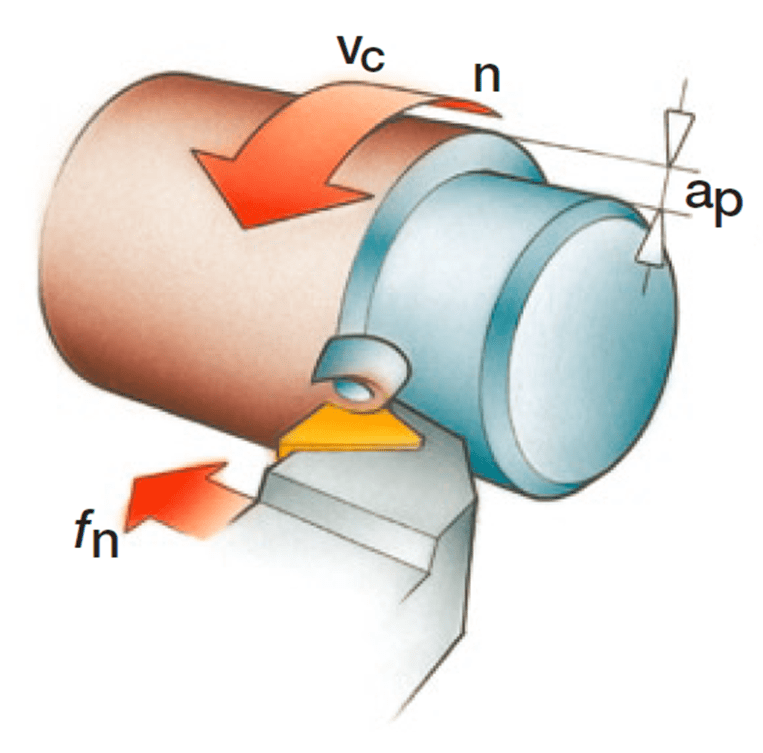
Turing Primary Motion
The tool remains fixed while the cylindrical workpiece rotates, creating the primary cutting motion.
Cutting speed (vc) (m/min)
Rotational speed (n) (rev/min)
vc = (n • π • Dc)/1000
Dc (mm) : Turning diameter (mm)
Turing Feed Motion
The tool moves laterally or longitudinally, creating the feed motion.
Feed speed (vf) (mm/min)
Feed per revolution (fn) (mm/rev)
vf = fn • n
Milling
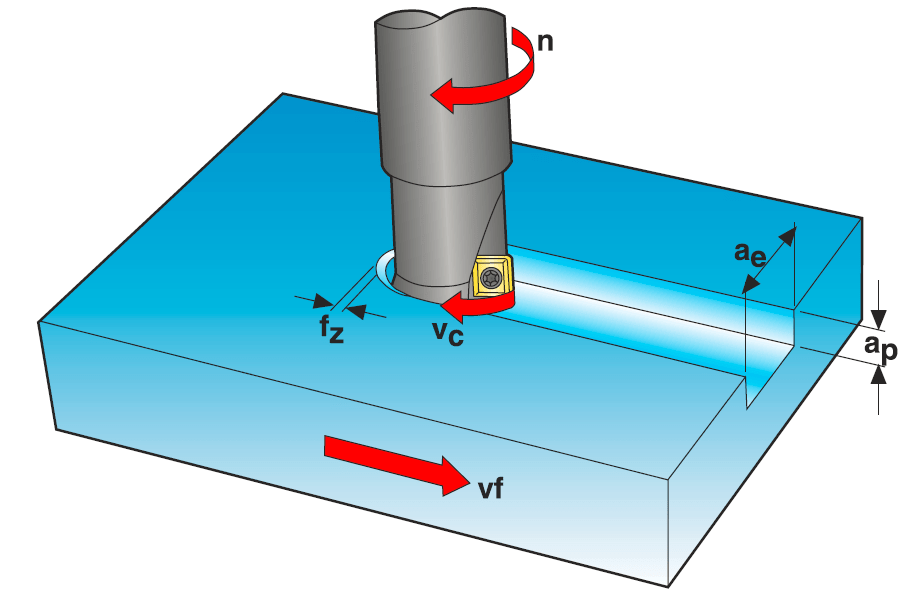
Milling Primary Motion
The tool rotates, creating the primary cutting motion.
Cutting speed (vc) (m/min)
Rotational speed (n) (rev/min)
vc = (n • π • Dc)/1000
Dc: Cutting edge diameter of the milling cutter (mm)
Milling Feed Motion
The workpiece moves linearly relative to the tool, creating the feed motion.
Feed speed (vf) (mm/min)
Feed per revolution (fn) (mm/rev)
Feed per tooth (fz) (mm/tooth)
vf = fn • n
fn = fz • zc
zc: Effective number of cutting teeth used to calculate the feed per revolution.
Drilling
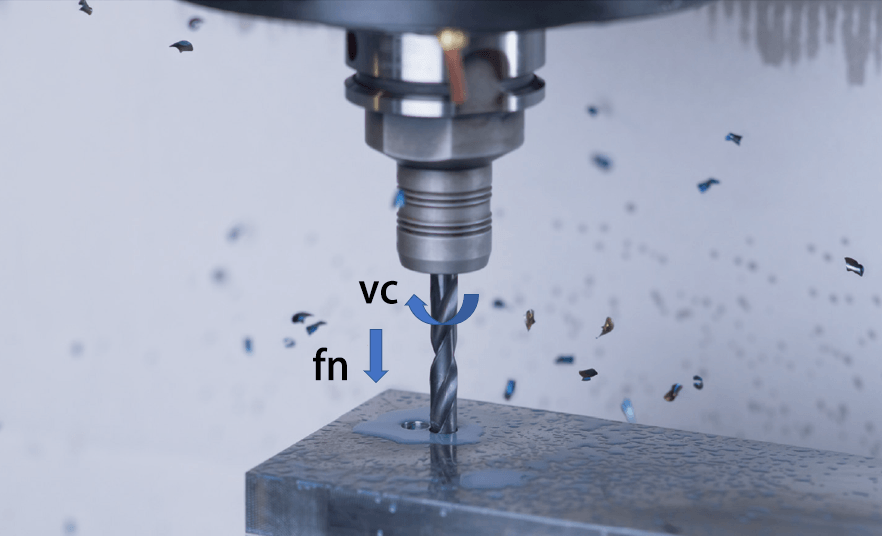
Drilling Primary Motion
The drill bit rotates, creating the primary cutting motion.
Cutting speed (vc) (m/min)
Rotational speed (n) (rev/min)
vc = (n • π • Dc)/1000
Dc: Diameter of the drilled hole (mm)
Drilling Feed Motion
The drill bit and the workpiece move linearly relative to each other, creating the feed motion.
Feed rate (vf) (mm/min)
Feed per revolution (fn) (mm/rev)
vf = fn • n
